How to Read Charger Parameters Like a Pro: Wattage, Voltage, Current & More
Ever looked at a charger and felt confused by all the numbers and symbols like “5V⎓3A” or “PD3.1 240W”? You’re not alone.
Whether you're a charger wholesaler, OEM buyer, or a tech-savvy brand, understanding these parameters is critical for choosing the right product for your devices or your customers. In this article, we’ll decode the key technical terms on chargers — and explain what they actually mean in real-world usage.

🔌 What Are Charger Parameters?
Charger parameters are the technical specifications printed on the charger’s label. They tell you how much power, voltage, and current the charger can deliver, and which charging protocols it supports.
Typical examples:
Input: 100-240V~50/60Hz 1.5A
Output: 5V⎓3A / 9V⎓3A / 20V⎓5A (100W Max)
Protocol: PD3.1, PPS, QC4+
Let’s break these down step-by-step.
⚡ Key Charger Parameters Explained
1. Wattage (W): Total Power Output
·Formula: Voltage (V) × Current (A) = Wattage (W)
·A 20W charger = 5V × 4A or 9V × 2.2A depending on configuration.
·Higher wattage = faster charging (if the device supports it).
Common Wattage Ranges:
·Smartphone: 18W–45W
·Tablet: 30W–65W
·Laptop: 65W–240W
2. Voltage (V): Electrical Pressure
·Measured in volts (V), it represents the charging level.
·Common levels: 5V, 9V, 12V, 15V, 20V.
·With PD 3.1, chargers now support 28V, 36V, and 48V — allowing up to 240W!
3. Current (A): Flow of Electricity
·Measured in amperes (A), it shows how much electricity flows.
·High current with low voltage = fast, cool charging.
·High current with high voltage = power for laptops & large devices.
4. Charging Protocols: How Devices Communicate
·PD (Power Delivery): Industry standard for USB-C fast charging.
·PD3.0 vs PD3.1: PD3.1 supports higher power (up to 240W).
·PPS (Programmable Power Supply): Allows dynamic voltage adjustment for ultra-safe and efficient charging.
·QC (Quick Charge): Qualcomm’s protocol, found in many Android phones.
🧪 Understanding Real-World Examples
| Charger Label | What It Means |
| 5V-3A | Basic fast charger (15W) -- typical for phones |
| 20V-5A | Hight-wattage (100W) -- ideal for laptops |
| 5V-3A, 9V-3A, 20V-5A | Multiple voltage steps -- adaptive PD charger |
※ Output gear (protocol difference)
The following lists the fast charging protocols that are most likely to correspond to each output gear and the backward compatible fast charging protocols. When making a judgment, it is recommended to first judge the private protocol based on the charger manufacturer, and then judge the public protocol of the charger. Because the charger page information is limited, it is usually impossible to indicate all the charging protocols of the charger. According to the information on its logo, only part of the fast charging protocol can be judged.
If you want to know all the charging protocols supported by the charger, you need to seek the help of a USB fast charging protocol tester. For those who do not have a tester, you can search for the corresponding evaluation of the charger on the Internet to find out.
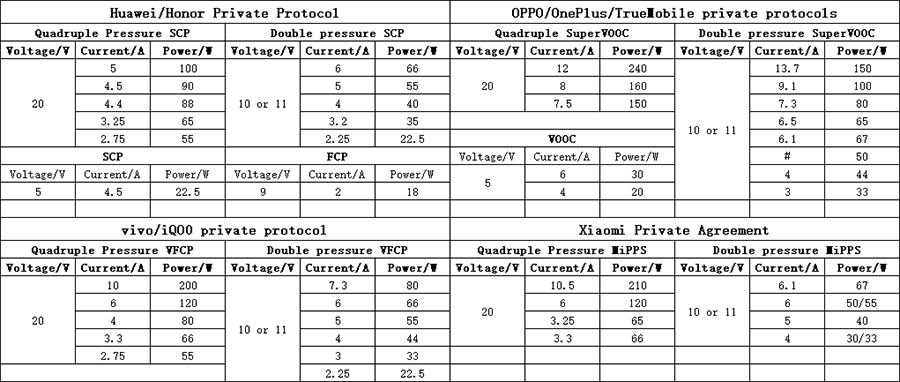
(1) Output gear of private protocol
The output gear of the private protocol needs to be judged in combination with the manufacturer of the charger. It is very simple. For example, Huawei's charger must be equipped with Huawei's private protocol as standard. The same is true for other manufacturers.
At the same time, all chargers are now backward compatible with low current gears under the same voltage. For example, the Realme 240W charger is marked as supporting "20V 12A". So while supporting 240W SuperVOOC, it is also backward compatible with 20V 8A and 20V 7.5A SuperVOOC protocols. It is also marked as supporting "11V 9.1A", which means it is compatible with other low current charging gears with double voltage from 11V 7.3A 80W to 11V 3A 33W. Other chargers are the same.
(2) Output gear of public protocol
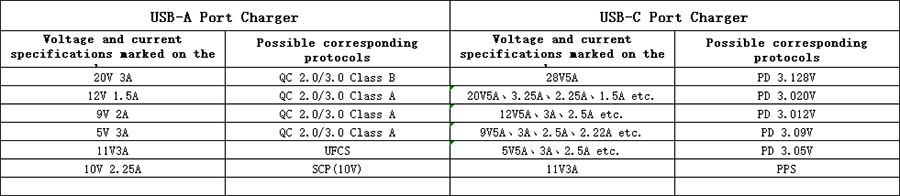
For chargers with USB-A ports (non-modified), the public protocol is mainly the QC protocol. Some chargers have the latest UFCS protocol. At the same time, because Huawei's 22.5W SCP protocol has been opened, many third-party chargers support it. If it is marked with 10V 2.25A, it is very likely Huawei SCP fast charging.
For USB-C chargers, the public protocol is mainly the PD protocol, and of course there is also the QC protocol. However, because the voltage levels of the QC protocol and the PD protocol are the same, the charger is generally not marked additionally, and further fast charging protocol testing is required to determine the level of the QC protocol.
If PDO: ×× is written on the output position of the charger, the voltage and current level behind it is the PD fast charging level. If PPS: ×× is written on the output position of the charger, the voltage and current level behind it is the PPS fast charging level. If the charger supports a 20V PD level, then it is likely that it can charge a laptop.
(3) Power and protocol allocation issues for simultaneous fast charging of multi-port chargers
When using multi-port chargers, power allocation issues are often encountered. At this time, it is necessary to pay attention to the maximum power that each port can output and the fast charging protocol supported when multiple ports are used at the same time. Generally, manufacturers will mark the maximum power supported by each port when multiple ports are output, and some will write in detail the supported voltage and current levels.
For example, when two ports of the Xiaomi 67W three-port charger are outputting at the same time, only one of them can handshake the PD fast charging protocol. However, when two ports of the UGREEN 45W dual USB-C port charger are outputting at the same time, both ports can handshake the PD fast charging protocol at the same time.
※ Charger Symbols
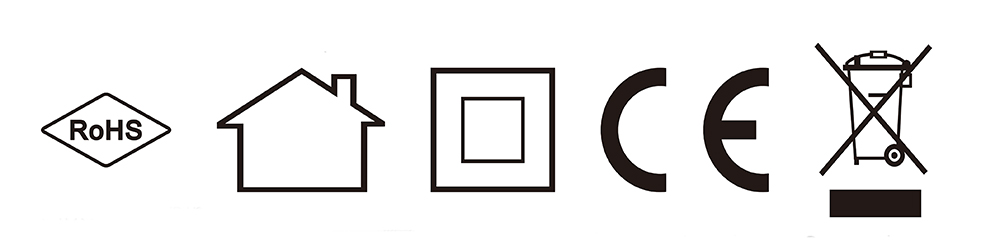
The five most common symbols, from left to right, are:
1. RoHS certification (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) ensures that electrical and electronic products comply with EU regulations by limiting the use of specific hazardous materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium.
2. Indoor use only symbol to prevent short circuits caused by rain outdoors.
3. Double insulation symbol, indicating that grounding protection is not required.
4. CE certification, which is the EU mandatory product safety certification mark. Chargers without CE certification are not recommended.
5. Do not discard symbol, which means that the charger should not be discarded in ordinary trash cans.
In addition, there are some other symbols: GRS, KC, FCC, UL, CCC, QC3.0 symbols, etc.
🏢 Why It Matters for B2B Buyers and Brands
If you're a charger distributor, brand, or wholesaler, knowing how to read charger specs lets you:
✅ Match the right charger to different markets (EU, KR, US)
✅ Communicate confidently with charger factories
✅ Avoid over-spec or under-spec purchases
✅ Design better product listings for your e-commerce store
✅ Ensure devices are safe and standards-compliant
🧩 OEM & ODM Projects: Spec Customization Tips
When working with charger manufacturers like Zonsan, here’s what you should prepare:
·Target devices (smartphones, laptops, etc.)
·Regional certification needs (CE, KC, ETL)
·Wattage range (e.g., 65W universal charger or 240W desktop charger)
·Port configuration (USB-C ×2, USB-C + USB-A, etc.)
·Protocol support (PD3.1, PPS, QC5)
📎 Related Blog Posts
PD3.1 240W Explained: What It Means for Your Next Charger
GaN vs PD Charger: What’s the Difference?
When using multi-port chargers, power allocation issues are often encountered. At this time, it is necessary to pay attention to the maximum power that each port can output and the fast charging protocol supported when multiple ports are used at the same time. Generally, manufacturers will mark the maximum power supported by each port when multiple ports are output, and some will write in detail the supported voltage and current levels.
For example, when two ports of the Xiaomi 67W three-port charger are outputting at the same time, only one of them can handshake the PD fast charging protocol. However, when two ports of the UGREEN 45W dual USB-C port charger are outputting at the same time, both ports can handshake the PD fast charging protocol at the same time.
※ Charger Symbols

The five most common symbols, from left to right, are:
1. RoHS certification (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) ensures that electrical and electronic products comply with EU regulations by limiting the use of specific hazardous materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium.
2. Indoor use only symbol to prevent short circuits caused by rain outdoors.
3. Double insulation symbol, indicating that grounding protection is not required.
4. CE certification, which is the EU mandatory product safety certification mark. Chargers without CE certification are not recommended.
5. Do not discard symbol, which means that the charger should not be discarded in ordinary trash cans.
In addition, there are some other symbols: GRS, KC, FCC, UL, CCC, QC3.0 symbols, etc.
🏢 Why It Matters for B2B Buyers and Brands
If you're a charger distributor, brand, or wholesaler, knowing how to read charger specs lets you:
✅ Match the right charger to different markets (EU, KR, US)
✅ Communicate confidently with charger factories
✅ Avoid over-spec or under-spec purchases
✅ Design better product listings for your e-commerce store
✅ Ensure devices are safe and standards-compliant
🧩 OEM & ODM Projects: Spec Customization Tips
When working with charger manufacturers like Zonsan, here’s what you should prepare:
·Target devices (smartphones, laptops, etc.)
·Regional certification needs (CE, KC, ETL)
·Wattage range (e.g., 65W universal charger or 240W desktop charger)
·Port configuration (USB-C ×2, USB-C + USB-A, etc.)
·Protocol support (PD3.1, PPS, QC5)
📎 Related Blog Posts
PD3.1 240W Explained: What It Means for Your Next Charger
GaN vs PD Charger: What’s the Difference?